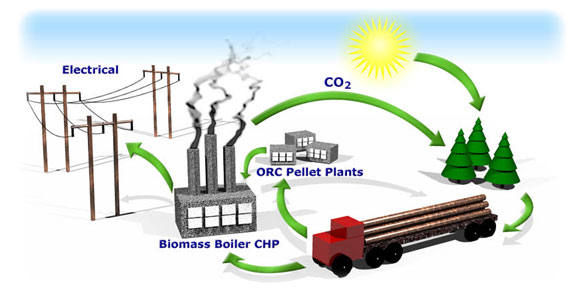
Bioenergy is the most widely used renewable energy worldwide and can be defined as "energy contained in living or recently living biological organisms" (fossil fuels are thus excluded). It can be differentiated into three different types of bioenergy:
Biomass contains stored energy. That's because plants absorb energy from the sun through the process of photosynthesis. When biomass is burned, this stored energy is released as heat.
Burning biomass releases carbon dioxide. However, plants also take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and use it to grow their leaves, flowers, branches, and stems. That same carbon dioxide is returned to the air when the plants are burned.
Many different kinds of biomass, such as wood chips, corn, and some types of garbage, are used to produce electricity. Some types of biomass can be converted into liquid fuels called biofuels that can power cars, trucks and tractors. Leftover food products like vegetable oils and animal fats can create biodiesel, while corn, sugarcane and other plants can be fermented to produce ethanol.
http://cleangreenenergyzone.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/biomass-energy.jpg
Types of Biomass Systems Used in Liberia
|
System |
Description |
Power range |
In Liberia |
|
The red fire pot that used a charcoal are produced by Liberians. By using the red fire pot, you can save money through slower burning coal. Fast cooking, long lasting, keeps your kitchen clean (no smoke, no ash and less heat).
|
280W/h |
Used in rural and urban areas in Liberia |
|
|
The Biomass Energy Plantthat use wood chips, coconut and palm kernel shells to produce clean and affordable energy for over 200 households and more than 2,500 residents of Kwendin.The Plant will also supply power to schools, churches and the business community. |
1000KWhydro-Electric plant |
Used in Liberia (Kwendin) NimbaCounty
|
For more information on Biomass visit Energypedia.
Wind power is the use of air flow through wind turbines to mechanically power generators for electricity. The Winds are caused by the uneven heating of the atmosphere by the sun, the irregularities of the earth's surface, and rotation of the earth. Wind flow patterns are modified by the earth's terrain, bodies of water, and vegetative cover. This wind flow, or motion energy, when "harvested" by modern wind turbines, can be used to generate electricity.
Wind power, as an alternative to burning fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable, widely distributed, clean, produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, consumes no water, and uses little land. The net effects on the environment are far less problematic than those of non-renewable power sources.
Wind farms consist of many individual wind turbines which are connected to the electric power transmission network. Onshore wind is an inexpensive source of electricity, competitive with or in many places cheaper than coal or gas plants. Offshore wind is steadier and stronger than on land, and offshore farms have less visual impact, but construction and maintenance costs are considerably higher. Small onshore wind farms can feed some energy into the grid or provide electricity to isolated off-grid locations.
People started using wind power centuries ago with windmills, which pumped water, ground grain and did other work. Today's wind turbine is a highly evolved version of a windmill. Modern wind turbines harness wind's kinetic energy and convert it into electricity. Most wind turbines have three blades and sit atop a steel tubular tower, and they range in size from 80-foot-tall turbines that can power a single home to utility-scale turbines that power hundreds of homes.
Wind is a type of renewable energy, and there are three major types of wind power namely:
For more information use these links:
https://energypedia.info/wiki/Portal:Wind
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_power
Bioenergy is the most widely used renewable energy worldwide and can be defined as "energy contained in living or recently living biological organisms" (fossil fuels are thus excluded). It can be differentiated into three different types of bioenergy: Biofuel, Biogas, Solid Biomass.
Burning biomass releases carbon dioxide. However, plants also take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and use it to grow their leaves, flowers, branches, and stems. That same carbon dioxide is returned to the air when the plants are burned.
Many different kinds of biomass, such as wood chips, corn, and some types of garbage, are used to produce electricity. Some types of biomass can be converted into liquid fuels called biofuels that can power cars, trucks, and tractors. Leftover food products like vegetable oils and animal fats can create biodiesel, while corn, sugarcane, and other plants can be fermented to produce ethanol.